Vapour Mitigation
Vapour Mitigation is the process of removing vapour phase contaminants to remediate a contaminated site or to protect receptors. Vapour Mitigation Systems (VMS) refers to active or passive systems that can be installed in a building to prevent entry of contaminated vapours to protect the indoor air quality.
Vapour Mitigation can be used remove almost every type of volatile contaminant. Some of the more common vapour contaminants are petroleum hydrocarbons (BTEX), and chlorinated solvents (PCE, TCE).
Several different technologies exist that use Vapour Mitigation to clean up contaminated sites:
- Soil Vapour Extraction (SVE) consists of active extraction of soil vapours from above the water table for aboveground treatment.
- Air Sparging (AS) consists of the injection of pressurized air below the water table to shift contaminants into the vapour phase, for extraction and aboveground treatment.
- In Situ Thermal Desorption (ISTD) consists of the introduction of intensive heat to aggressively volatilize contaminants into the vapour phase for extraction and aboveground treatment.
Passive vapour mitigation systems typically consist of a physical barrier that prevents vapours from migrating up into a building. Active systems typically consist of a sub-slab depressurization system (SSDS) that changes the vapour pressure beneath a building by actively extraction vapours. In some cases, both passive and active systems are required at the same building for protection of indoor air quality.
Yes, vapour mitigation systems can be installed within existing buildings through custom retrofit design.
Vapour Mitigation Methods
A variety of methods exist, with their own benefits, limitations, and specifications.
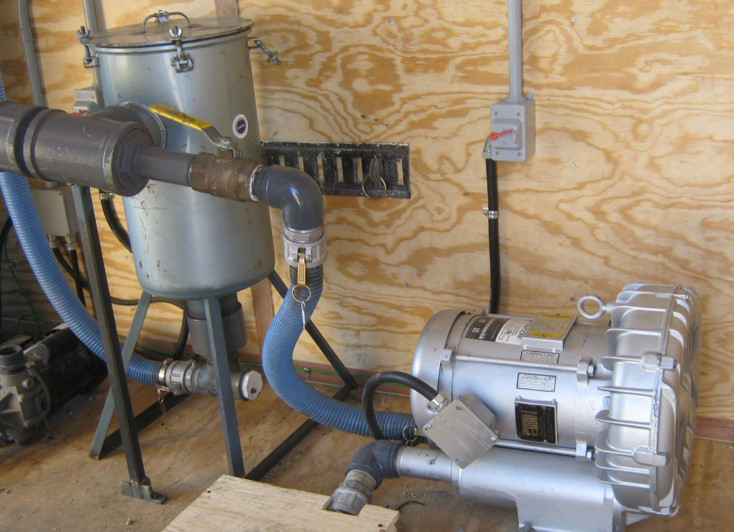

Soil-Vapour Extraction (SVE)
Soil-Vapour Extraction consist of active extraction of soil vapours for aboveground treatment via adsorptive media or catalytic oxidation.
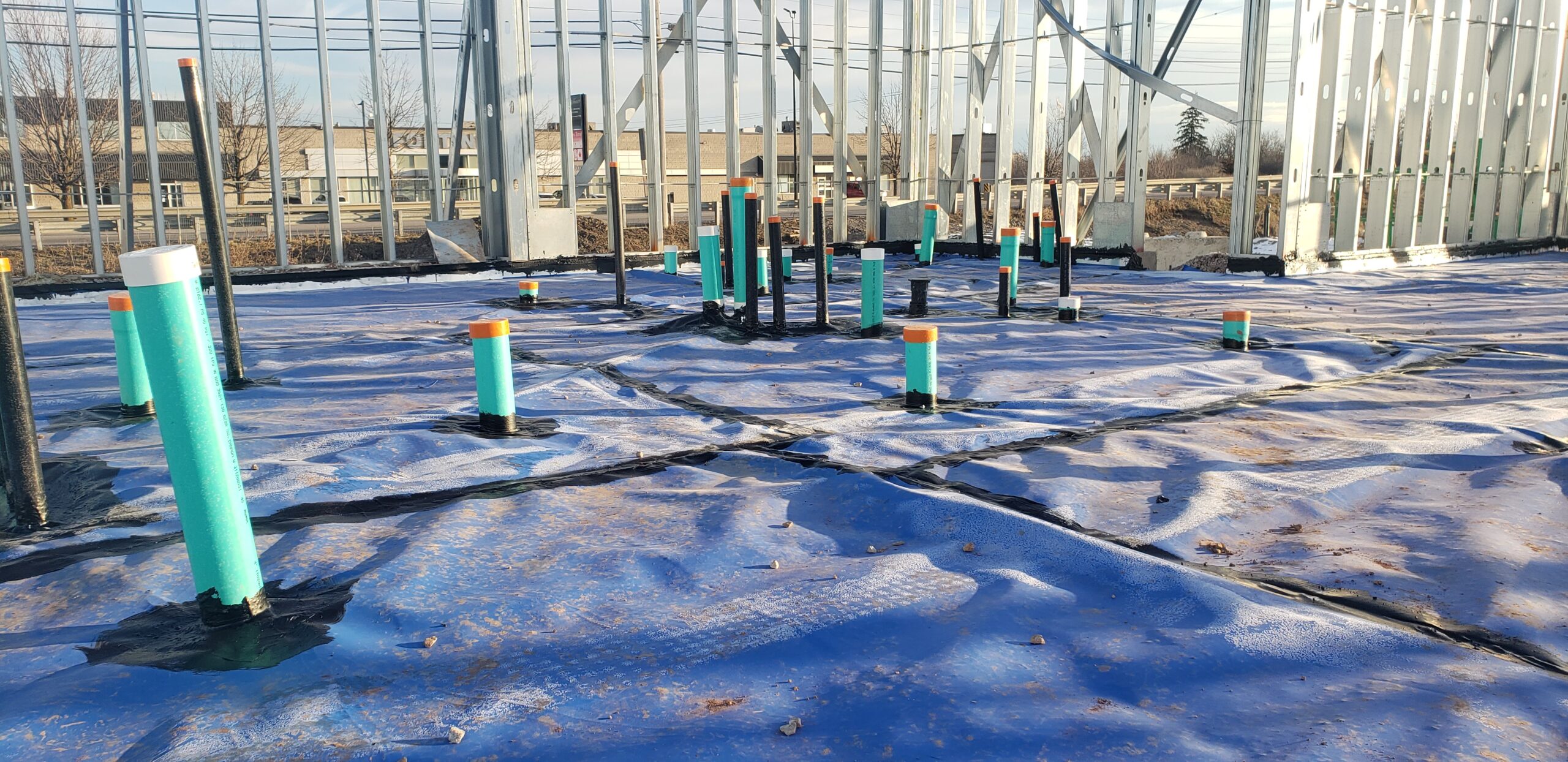

Vapour Mitigation Systems (VMS)
Vapour Mitigation Systems are active or passive systems installed on new or existing buildings for the protection of indoor air quality.
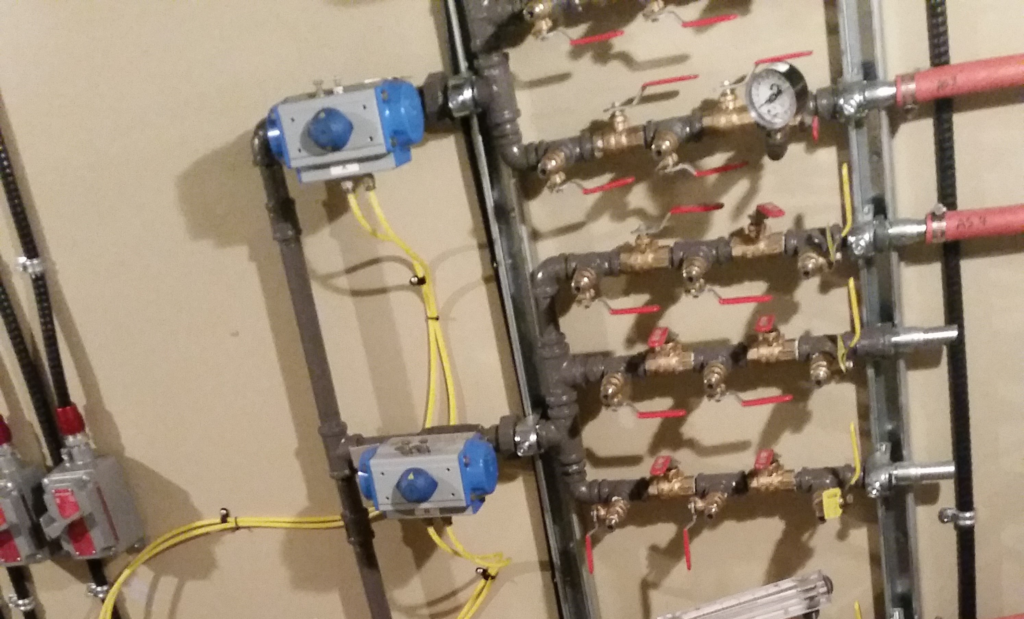
Air Sparging (AS)
AS consists of the injection of pressurized air below the water table to shift contaminants into the vapour phase for extraction and treatment. Biosparging, similar to Air Sparging, consists of the introduction of a low flow of air to promote aerobic biodegradation of contaminants.
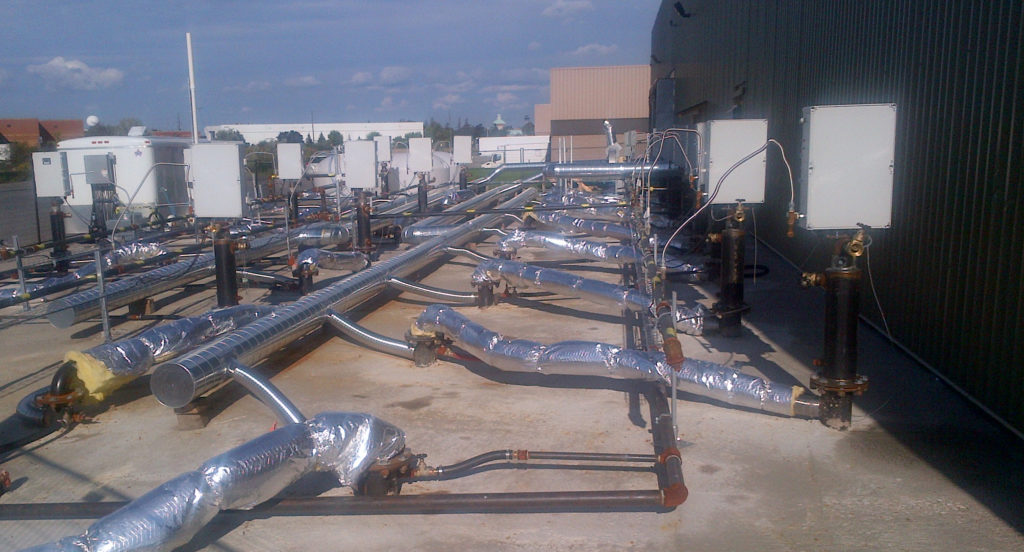

In Situ Thermal Desorption (ISTD)
In-Situ Thermal Desorption systems consist of the introduction of intensive heat to aggressively volatilize contaminants into the vapour phase for extraction and treatment.
Benefits of Vapour Mitigation Systems
Vapour Mitigation Systems (VMS) have many benefits, including:
- Health: VMS’s are used to address the risk of contaminated vapours, and allow the continued use of buildings that would otherwise be unsafe for human occupancy
- Cost: VMS technologies can provide a very cost-effective approach to remediate volatile contaminants, protecting indoor air quality.
- Time: VMS’s can provide protection around the clock with very little maintenance or downtime

Tools & Experience
Vertex combines theoretical understanding with practical experience for the piping layout, installation and optimization of various types Vapour Mitigation Systems.
Expedite your project timeline by using one of Vertex’s mobile Environmental Compliance Approvals (ECAs) to permit the extraction of contaminated vapours, and treatment via either adsorptive media or catalytic oxidation.
Discuss options with Vertex today to understand what type of system is best suited for your property.